How Much Does Dog Salivary Gland Surgery Cost?
Last Updated on November 23, 2023
Written by CPA Alec Pow | Content Reviewed by ![]() CFA Alexander Popinker
CFA Alexander Popinker
A salivary cyst is a common disease in dogs. Veterinarians say that these mandibular gland cysts can be found under the dog’s jaws or in its mouth. They can be small or large (about the size of a grapefruit). The growth appears as a swelling under the neck. Sometimes these swellings can be caused by abscesses, tooth infections, tumors, or gum wounds, but most of the time they are caused by the salivary glands.
If a dog has a cyst, the best treatment a dog needs is surgery. Therapy does not always give results. There are only rare situations in which some medications have given results. If the salivary gland has been blocked for a while, things return to normal, but if it has ruptured, then surgery is needed. Surgeries are necessary where the saliva flows past the adjacent tissues. When a dog has a cyst full of saliva under the jaw, the salivary glands on the affected side are all removed.
How Much Does Dog Salivary Gland Surgery Cost?
You should expect to pay anywhere between $700 and more than $3,800 for dog salivary gland surgery, including the hospitalization days and testing in a medical veterinary clinic. Regardless of the type of diagnosis, in general, vets will recommend surgery to remove the ruptured glands involved.
However, this is considered a temporary solution. There are several factors that will affect the cost of salivary gland surgery for a dog, such as the pre-operative and post-operative work your pet requires, your geographical location, the vet you choose, and the type of diagnosis.
You might also like our articles about the cost of ear hematoma surgery, slipped disc surgery, and entropion surgery in dogs.
According to a post on the Wag Walking website, the cost of a dog salivary gland surgery is around $2,600, but you can also find cheaper options.
From discussions on the online forum German Shepherds, we found that the cost of a dog salivary gland removal surgical procedure is around $3,200.
If you want to take your dog to the Helping Hands Vet in Richmond, Virginia, you should be prepared to pay around $750 for a salivary gland removal surgery.
Additional costs of sialoadenectomy procedure in dogs
The initial quote offered by your vet may or may not include the costs of tests performed before the surgery. In order to see if the dog is able to handle the anesthesia during the surgery, your vet will ask for X-rays to locate the affected salivary gland, draw blood, and take a sample of his urine.
In case the surgery is very complex, your vet may want to monitor your pet’s health state overnight for the following 24 to 48 hours. In order to cope with the pain after the surgery, your vet will also prescribe pain medication for controlling the pain, as well as local anesthetics, and/or anti-inflammatories.
In general, a few weeks after the procedure a follow-up appointment will be necessary to remove the drain and check on the incision.
Surgical procedure overview
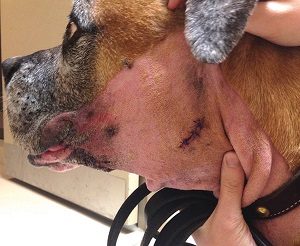 First, the cyst is opened, the fluid and excess tissue is removed, and then the skin is closed. The second step consists of removing the affected salivary ducts. The glands that remain unaffected will have to take over the activity of those that are removed. Although it seems like an easy thing to do, it is actually very difficult due to the nerves and blood vessels that are in this area.
First, the cyst is opened, the fluid and excess tissue is removed, and then the skin is closed. The second step consists of removing the affected salivary ducts. The glands that remain unaffected will have to take over the activity of those that are removed. Although it seems like an easy thing to do, it is actually very difficult due to the nerves and blood vessels that are in this area.
The surgery is conducted under general anesthesia and involves suturing and drainage. Post-op antibiotics and anti-inflammatory meds are administered for up to four days following surgery.
Post-surgery care with a bandage is important to ensure your dog’s incision site heals properly and to prevent infection or complications. The recovery period takes several weeks as proper chewing function is restored. Complete excision of primary glands aims to prevent recurrence.
For puppies that have a cyst under the tongue, the operation is easier: the cyst is opened and its walls are basically turned inside out and sutured down towards the buccal mucosa. A ruptured pouch will be created which will gradually heal forming a new opening for the salivary duct. Following this operation, the salivary glands are not affected.
It is very important that quadrupeds that have cysts are taken by their owners to the veterinarian. If the owner of the puppy waits too long, it will be very difficult for the veterinarian to figure out where the problem started. For the health of your puppy, go to the vet as soon as you notice that the four-legged friend has a cyst.
Symptoms
- Difficulty in breathing, even during periods of rest. In addition, a constant irritation of the mouth and pharynx can cause an animal to gag (a reflex that resembles the effort to vomit).
- The inflamed glands increase in size. Sometimes they can collect pus.
- Increase in body temperature. As with any other form of inflammation, the dog’s body temperature rises. A mild fever is possible.
- Excessive salivation leads to dehydration of the animal and severe weight loss. In this context, nervous disorders can manifest, and aggressive behavior worsens.
Disease diagnosis
Any inflammation of the salivary glands in dogs requires a thorough diagnosis. This is necessary not only to establish the correct treatment but also to exclude the presence of malignant tumors in the mouth. During the diagnosis, the doctor must collect all the information about the animal: other diseases, medical procedures performed, the animal’s preference for eating grass and garbage, etc.
Since the animal is in pain during the examination and often behaves aggressively, general anesthesia is applied. This gives the doctor the opportunity not only to conduct a thorough examination but also to collect all the necessary samples for tests.
Types of dog salivary glands
There are three pairs of major salivary glands: parotid, mandibular, and sublingual glands.
- The mandibular gland of dogs is located along the sides of the jaw, close to the back of their mouth, between the two veins. This is a fairly large oval organ of a yellowish color.
- The parotid glands are located in the ear region. They are relatively small, and their canals pass over the muscles of mastication.
- The sublingual gland, as the name suggests, is under the tongue. The fluid secreted by each gland is different in its composition and functions. Therefore, the inflammation of any of them leads not only to unpleasant sensations for the dog but also to problems in the entire cycle of the digestive process.
Important things to consider
Most often, problems with the salivary glands occur both in young puppies and in representatives of certain breeds: poodles, boxers, German shepherds, and dachshunds. The loading of the salivary glands is most often manifested by an increase in salivation. The dog often begins to swallow the disturbing fluid. Excreted saliva may have an unpleasant odor.
The inflammatory process is quite intense. It can move into neighboring areas and cause problems with the dog’s swallowing and breathing.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!