How Much Does Esophageal Dilation Cost?
Esophageal dilation, also called pneumatic dilation, is a medical approach that enlarges a portion of the esophagus to allow the patient to swallow more easily.
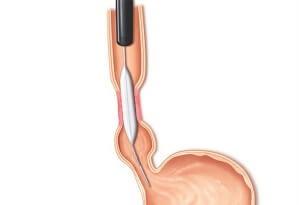
The esophageal dilation procedure is required when the patient has difficulty swallowing or dysphagia, caused by tissue inflammation in the esophagus, scarring caused by acid reflux, and other possible health issues. An endoscopic tube will be inserted through the patient’s mouth, into the esophagus, where a dilating balloon or plastic dilator will widen the appropriate section.
How much does esophageal dilation cost?
The cost for an esophageal dilation procedure is anywhere from $100 to $3,500. Take into consideration that the cost will greatly depend on whether the patient has health insurance or not.
For example, if there is no health coverage, the patient will pay between $1,500 and $3,500. The cost range will depend on the complexity of the procedure, your geographical location, the hospital or doctor’s office where the procedure is performed, and other expenses.
MDSave.com states that the average cost for an esophageal dilation in the United States can be around $2,621, while their national average cost is $1,446. These costs will vary based on your geographical location and other factors. Also, MdSave claims that their cost range for this procedure is anywhere from $1,235 to $2,222.
According to Medicare.gov, the average cost in an ambulatory surgical center is around $118 while in a hospital outpatient department, the cost will be around $198, on average, as long as you have Medicare coverage.
YourCommunityHospital.com, claims that the cost range can be anywhere from $1,900 up to $3,000 per procedure.
One member of the Boards.StraightDope.com forum stated that the procedure can cost around $2,500. However, it may reach up to $4,700, if the doctor’s and anesthetist’s fees are charged separately.
Esophageal dilation overview
If your doctor determines that esophageal dilation is required to treat the patient’s health condition, he will first inform them how to prepare for the procedure. For instance, the physician will recommend them not to eat or drink before the procedure, in order to have an empty stomach.
The procedure will be done on the patient while they are sedated. A local anesthetic spray will also be applied on the throat, to numb it and to reduce discomfort.
First, a mouthguard will be positioned between your teeth, to ensure that your mouth will be opened during the procedure. Then, an endoscope, a flexible tube with a camera, will be introduced in the mouth, then down the esophagus, to locate the narrowed section.
You might also like our articles about the cost of video capsule endoscopy, thyroid ultrasound, or tonsil removal.
Once the section with issues is located, the doctor will introduce a catheter down the throat which will be inflated, to widen the issued area. While this is done, the patient will feel no pain. Some pressure might still be experienced.
Finally, the doctor will use the endoscope again to examine the dilated section, the stomach, and the duodenum.
Once the esophageal dilation procedure is completed and the patient has recovered from the sedative, he or she can go home later on the same day.
Common side effects after the procedure may be sore throats, mild chest discomfort, and abdominal bloating. Usually, these sensations will disappear within a few hours.
Esophageal dilation is said to last 20 minutes on average.
What to expect after esophageal dilation
After the esophageal dilation, the patient will be moved to a recovery room to be monitored until the sedative’s effect fades. Typically, the patient spends around two hours to recover and be able to go home in a safe way.
Driving after the procedure is forbidden for the next 24 hours, or at least until the sedative fades completely.
As per the alimentation, the patient will be able to stick to a normal diet, but if there are sensations of a sore throat it is recommended to consume soft food and liquids for the next 24 hours.
Reasons you may need esophageal dilation
- Acid Peptic Stricture – This is one of the most common conditions, where gastric acid, produced by the stomach, will reflux in the esophagus causing burn-like sensations, inflammations, and scars on the throat. Over time, the scars caused by acid reflux may narrow the esophagus. If any hiatus hernia is present, the condition will get aggravated.
- Schatzki’s Ring – This is a thin, benign, circular tissue that forms on the lower section of the esophagus, contracting the area.
- Achalasia –Achalasia means failure to relax and is the rarest condition. With this disorder, the smooth muscle does not function properly and cannot relax, making the lower esophageal sphincter contract and remain closed. The esophageal contents trickle slowly into the stomach due to a persistent blockage.
- Ingestion of Caustic Agents – Swallowing liquids that contain caustic agents, will severely damage the esophagus. These chemical agents will burn the esophagus, creating serious scarring that will lead to a narrowed throat.
- Tumors – The presence of a form of tumor, whether it may be benign or malignant, can cause the esophagus to block. It is crucial to promptly diagnose and treat this condition.
- Heredity – There may be cases when patients are born with a partial or complete blocked esophagus.
What are the extra costs?
 Typically, general anesthesia is required, which may cost around $1,800, if the patient isn’t covered by health insurance.
Typically, general anesthesia is required, which may cost around $1,800, if the patient isn’t covered by health insurance.
An endoscopy procedure is required while performing an esophageal dilation and this can add an extra $700 to $2,000 to your overall cost.
X-rays may be required before the doctor dilates the esophagus. This may be an additional cost to take into account.
There are cases when one esophageal dilation may not be enough, depending on the patient’s immune system, the cause of the problem, and recovery. Another procedure may be required in the future in the case of a gastrointestinal complication, which will heavily increase the budget.
Acid-suppressing medications may be prescribed by the doctor when the cause of the narrowing is acid reflux. These medications are to prevent future problems.
Important things about the dilation procedure
It is recommended not to eat and drink at least six hours before esophageal balloon dilation.
Driving after the procedure is forbidden for at least 24 hours or until the sedative is out of the patient’s system. The sedatives may make the patient lightheaded and sleepy.
Avoid consuming alcohol for the next 24 hours.
It is recommended to take small bites of food and chew it thoroughly while eating during the recovery.
Also, eat small amounts of food at a meal, but eat more often.
If you have health insurance, make sure to go over everything with your insurance provider as the patient is only responsible for their co-pay and deductibles if the procedure is considered medically necessary.
How can I save money?
In case there is no health insurance coverage, try talking to the hospital’s finance department about this aspect. They may provide discounts if the procedure will be paid upfront in cash.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!