How Much Does Tubal Ligation Cost?
Last Updated on May 9, 2024
Written by CPA Alec Pow | Content Reviewed by ![]() CFA Alexander Popinker
CFA Alexander Popinker
Tubal ligation is a common permanent contraception method for women who want to prevent future pregnancies. But like most medical procedures, there are costs to consider.
This in-depth article will examine the factors influencing tubal ligation prices, including surgical methods, healthcare provider, insurance coverage, and geographical location. Understanding these elements can help women budget and plan for this procedure.
How Much Does Tubal Ligation Cost?
Tubal Ligation procedure has a base cost that can range widely from $2,000 to $8,000 with location, setting and insurance affecting prices.
There are a few different surgical approaches to tubal ligation, which can impact the overall cost:
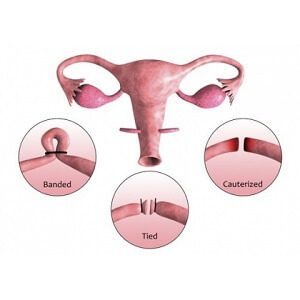
Laparoscopic tubal ligation uses a thin, lighted tube and tiny incisions to access and cut or tie off the fallopian tubes. This is the most common approach, with typical costs of $2,000 to $6,000.
The procedure takes 20-30 minutes and involves smaller incisions, resulting in faster recovery. Performing it as outpatient surgery helps reduce costs as well.
Minilaparotomy involves a small abdominal incision to cut or tie the tubes. It has a similar cost range of $2,500 to $5,500 on average.
Though slightly more invasive than a laparoscopy, a minilaparotomy is still an outpatient procedure with minimal recovery time. Operating room costs are modest for this approach.
A salpingectomy fully removes the fallopian tubes instead of just blocking them. It is more invasive, with average costs of $3,000 to $7,000.
Removing the tubes requires general anesthesia and a longer OR time, driving up costs. But it may have lower failure rates than ligation procedures.
The surgical facility, specialist fees, anesthesia, and aftercare contribute to the overall price as well.
According to MDsave, the cost of a laparoscopic tubal ligation ranges from $4,808 to $11,393.
Planned Parenthood reports that tubal ligation can cost between $0 to $6,000, including follow-up visits. The cost can vary depending on the location, type of procedure, and insurance coverage.
GoodRx indicates that the median costs for laparoscopic tubal ligation range from $2,880 to $5,163. They also provide examples of cash-pay prices, such as $3,000 to $4,000 near Beverly Hills, California, and $6,145 to $9,218 for a 40-year-old woman without insurance in the Houston area.
WebMD states that tubal ligation surgery can cost $500-$5,000 or more, with the cost varying based on location, type of surgery, doctor, and insurance coverage.
Tubal Ligation Overview
Tubal ligation, also known as “getting your tubes tied,” involves blocking or severing the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy. It is a surgical procedure done under general anesthesia, either through open abdominal surgery (laparotomy) or minimally invasive laparoscopy.
Tubal ligation is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy and is considered a permanent form of birth control. The procedure is relatively safe, with few complications or side effects. Many women choose tubal ligation when they are certain they do not want more children.
Why Women Choose Tubal Ligation
There are several reasons women may seek tubal ligation:
- They do not want any more children
- Other contraceptives have intolerable side effects
- Their partner has refused a vasectomy
- Medical contraindications prevent using contraceptives
- They want highly effective pregnancy prevention
- They want the convenience of a permanent solution
Careful consideration of the permanent implications is necessary before getting this procedure.
Impact of Geographic Location
Location is a major cost factor for tubal ligation. Cost of living, healthcare market conditions, and population demographics all influence pricing.
Urban areas with higher costs of living will have higher average tubal ligation prices.
In expensive metropolitan cities like New York and San Francisco, average costs exceed $6,000. Specialists in these areas charge higher rates.
Smaller towns and rural areas typically have lower healthcare costs across the board, reflected in tubal ligation prices averaging $2,000 to $4,000. Competition between hospitals and surgical centers helps keep prices down.
It is always smart to compare costs from different providers in your region to find the best value. Looking within a 50-mile radius can reveal pricing differences.
Cost Ranges by Location
Here are typical tubal ligation cost ranges based on location:
- New York City: $6,000 – $8,000
- Chicago: $3,000 – $5,000
- Austin, TX: $2,500 – $4,500
- Portland, ME: $3,500 – $6,000
- Jacksonville, FL: $2,000 – $4,000
- Billings, MT: $1,500 – $3,500
As shown, major metropolitan and coastal areas tend to have the highest prices.
Inpatient vs Outpatient Settings
Tubal ligation can be performed either as an inpatient procedure at a hospital or outpatient at an ambulatory surgery center.
Inpatient tubal ligations average around $4,000 to $8,000 depending on the facility and length of stay. Hospital operating rooms are more expensive.
Outpatient procedures typically cost $2,000 to $5,000 since they require less recovery time. Many providers now favor outpatient tubal ligation for its convenience and cost savings.
You might also like our articles about the cost of a pelvic ultrasound, vasectomy, or IUD removal.
When possible, having the procedure at an outpatient clinic is the most affordable option. Yet hospitals provide safety for complex cases.
Price Difference Examples
- Local hospital inpatient: $7,500
- Surgical center outpatient: $3,000
- University hospital inpatient: $10,000
- Planned Parenthood outpatient: $2,000
As shown, outpatient centers offer significant savings over hospitals.
The Role of Health Insurance
Insurance coverage significantly impacts what you will pay out of pocket for tubal ligation. Those without insurance face the full costs, while covered patients pay a fraction.
Most insurance plans cover tubal ligation, but deductibles ($1,500 on average) and coinsurance (20% typical) apply. Smaller copays like $20-$50 for the specialist visit are also common.
With insurance, out-of-pocket costs for tubal ligation may range from $500 to $2,000 depending on the plan details. Uninsured patients pay the full surgical fees.
Sample Covered Costs
- Laparoscopic tubal ligation cost: $5,000
- Plan deductible: $1,000
- Coinsurance: 20%
- Total out-of-pocket cost: $1,000 + 20% x $4,000 = $1,800
The insured patient saves significantly compared to covering the full $5,000 cost.
Financial Assistance Options
 For low-income women, financial assistance is available to reduce tubal ligation costs through Medicaid and other programs.
For low-income women, financial assistance is available to reduce tubal ligation costs through Medicaid and other programs.
Medicaid covers family planning services like tubal ligation at no cost in most states. Enrollment is based on income.
Title X clinics, like Planned Parenthood, offer free or discounted services based on income eligibility. This includes tubal ligation.
Local and national non-profits may provide grants and funding to cover sterilization costs for women in financial need.
In addition, many hospitals and clinics offer income-based discounts or sliding fee scales. Checking with local providers is always advised.
Sample Aid Programs
- Medicaid – Covers 100% of costs for enrollees
- Planned Parenthood – Offers tubal ligation on sliding fee scale based on income
- Gates Foundation – Provides tubal ligation funding for low-income women
Additional Cost Considerations
When budgeting for tubal ligation, women should consider potential additional costs:
- Consult visit: $75-$200 for the initial consultation to discuss the procedure
- Anesthesia fees: $500-$1,500 depending on if hospital or ASC-based anesthesiologist
- Postoperative care: Follow-up visits to monitor recovery may cost $100-$300
- Complications: Treatment for rare issues like bleeding or infection can cost hundreds or thousands
Building in a buffer for unforeseen expenses is wise when saving up for this procedure. Having at least $1,000 available for incidentals is prudent.
Contraceptive Alternatives
There are other permanent and non-permanent contraceptive options that have different cost considerations:
- Vasectomy: $350-$1,000 out of pocket but covered by insurance
- IUD device: $0-$1,300 depending on insurance coverage
- Contraceptive implant: $0-$1,200 based on insurance coverage
- Tubal ligation reversal: $5,000-$15,000 if reversal is later desired
Over a lifetime, tubal ligation may be more cost effective than continuous costs for prescription birth control, condoms, or emergency contraception. Weighing long-term costs against convenience is important.
Sample Lifetime Cost Comparison
- Tubal ligation: $2,000-$5,000
- Birth control pills for 30 years: $15,000-$30,000
- Condoms for 30 years: $5,000-$15,000
Tubal ligation comes out favorably when taking the long view.
Insurance Coverage Landscape
Most private insurers and government programs cover tubal ligation:
- ACA compliant plans cover with no out-of-pocket costs when using in-network providers
- Medicaid covers full costs for tubal ligation in nearly all states with minimal co-pays
- Medicare covers 80% of costs for those age 35+; 20% coinsurance applies
- Employer plans typically cover tubal ligation with annual deductible and coinsurance
But gaps exist, so verifying benefits is essential. Religious employers may request exemptions from contraceptive coverage.
The Healthcare and Insurance Landscape
The healthcare and insurance environment also impacts costs for procedures like tubal ligation.
Rising costs for facilities, provider services, drugs and medical technology all contribute to inflation in healthcare spending. Hospitals and clinics must cover these increasing expenses through higher procedure fees.
Consolidation in the insurance industry also reduces competition. Lack of payers means providers have less incentive to curb rate hikes.
But the Affordable Care Act has expanded contraceptive coverage. Cost is less of an access barrier than in past decades before birth control coverage was mandated.
Price Transparency in Healthcare
Many hospitals and surgery centers are beginning to provide price transparency tools to allow consumers to compare costs for procedures like tubal ligation.
Online cost comparison tools publish price lists and discounted cash rates to attract patients. This transparency allows women to shop around for the best value.
However, opaque insurance billing practices still make it difficult to get full clarity on out-of-pocket costs. Navigating deductibles, copays and coinsurance remains challenging.
Patient advocate groups push for laws requiring upfront cost estimates for nonemergency care like a tubal ligation. But enforcement lagged. Patients must still actively seek pricing data.
Final Words
Financial assistance from Medicaid and clinics is available for low-income women to improve affordability. Healthcare inflation and insurance hurdles contribute to high prices, but policy advances are improving transparency.
Considering lifetime costs versus temporary contraceptive methods provides helpful perspective.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main disadvantage of tubal ligation?
The main disadvantage of tubal ligation is that it is meant to be a permanent form of birth control. For women who later change their minds and want to have more children, tubal ligation reversal is expensive and not always successful.
The procedure is considered permanent sterilization, so women must be certain before having their fallopian tubes tied.
What are the restrictions after a tubal ligation?
There are few lifestyle restrictions following tubal ligation. Recovery takes about 1 week, involving rest and avoiding strenuous activity. Sex can typically resume after 1-2 weeks.
The only major restriction is that pregnancy is much less likely due to the blocked fallopian tubes. But you must continue using contraception until a semen analysis confirms sperm are no longer present. There are no restrictions around physical activities, exercise, travel, or work. Most women can resume normal activity within 7-10 days.
Do people regret getting their tubes tied?
Some women do come to regret permanent tubal ligation, especially younger patients who later want to have more children. Estimates indicate 5-20% of tubal ligation patients eventually pursue reversal.
Reasons for regret include change in marital status or new partner, death of a child, or renewed desire for more children. But for women over 30 who do not want more children, studies show high satisfaction rates of over 90% after tubal ligation. Careful consideration of the permanent implications is wise before any sterilization procedure.
Is tying your tubes 100% effective?
Tubal ligation is over 99% effective at preventing pregnancy when performed correctly. In rare cases, the tubes can reconnect on their own over time, allowing for possible conception. The failure rate is incredibly low at just 0.2-0.8% after 5 years.
When pregnancy does occur following tubal ligation, it is higher risk due to likelihood of ectopic pregnancy. But for most women, tying the tubes permanently prevents conception for the rest of their lives. Those considering reversal should not bank on full fertility restoration.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!