Fibroid Surgery Cost
Last Updated on August 16, 2022
Written by CPA Alec Pow | Content Reviewed by ![]() CFA Alexander Popinker
CFA Alexander Popinker
Uterine fibroma is the most common benign tumor that develops in the muscular layer of the uterus. The appearance and development of uterine fibroids are influenced by the monthly hormonal fluctuations present in the case of fertile women, with approximately 40% of women over 35 years old being diagnosed with this condition.
In certain situations, genetic factors of the disease or related to the patient’s lifestyle have also been identified (hormonal treatments, the number of pregnancies throughout life, body weight – overweight women show an increased incidence of the disease).
How Much Does Fibroid Surgery Cost?
In case you don’t have health insurance, you should be prepared to spend anywhere between $10,000 and more than $42,000 for fibroid surgery. For instance, the cost of a hysterectomy will start at around $16,000 and go up to more than $26,000, while for a uterine fibroid embolization you will have to pay anywhere between $10,000 and $16,000. When other treatments have been exhausted and the fibroid surgery is deemed medically necessary, the costs of the surgery will be covered by health insurance.
You might also like our articles about the cost of tubal ligation, pilonidal cyst surgery, or an Ob/GYN visit.
According to a study realized by NCBI, the cost of a hysterectomy is around $16,500 and the non-surgical treatment is almost $7,500.
From the Fibroid Relief website, we found out that the cost of a myomectomy is around $20,000.
In the table below you will find the average costs of different fibroid treatment options.
| Treatment Option | Price (without insurance) |
| UFE (Uterine Fibroid Embolization) | $16,000 to $43,000+ |
| Myomectomy | $14,000 to $27,000 |
| Hysterectomy | $16,000 to $34,000 |
| Endometrial Ablation | $10,000 to $22,000 |
Fibroid surgery options
Surgical treatment is indicated in the presence of significant bleeding accompanied by anemia, large uterine formations, infertility, or a history of lost pregnancies and is represented by:
- Total hysterectomy – total removal of the uterus;
- Uterine artery embolization – used in patients who no longer want children but do not want a hysterectomy;
- Myomectomy – removal of formations with the preservation of the uterus used in patients who want pregnancies in the future;
- Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery, after which thermal destruction of fibroids is obtained;
- Myolysis – thermal or cryoablative coagulation of fibroids;
- Endometrial ablation – removal of the lining of the inside of the uterus to control heavy bleeding.
Fibroid drug treatment options
Drug treatment options are represented by:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues – GnRH represent treatment with effective results in reducing the volume of uterine fibroids for easier surgical removal; it is not a therapy that can be used in the long term, the interruption of the medication causing the reappearance of the symptoms, and the increase in the volume of the fibroid in a few months;
- Hormonal therapy that is administered with the aim of reducing blood loss;
- Progesterone receptor modulators have a similar effect to gonadotropin analogues, but show lower adverse effects;
- Administration of androgenic steroids can be beneficial in certain situations but not with few side effects;
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs relieve pain.
- Antifibrinolytic agents reduce blood loss;
What are the additional expenses?
Before even taking into consideration surgery, a doctor will have to diagnose the patient in order to confirm they have fibroids. This can be done by going through certain tests like a biopsy, an ultrasound, a laparoscopy, and/or a hysteroscopy. In general, the most common test administered is an ultrasound which will be taken when the patient goes through difficult periods. In order to take a closer look at the uterus a transvaginal scan will be taken, while a hysteroscopy will be used for examining the inside of the uterus. If needed, a biopsy will be performed to take a small sample of the uterus lining.
Most of these procedures will require painkillers for the following three to six weeks.
Important things to consider
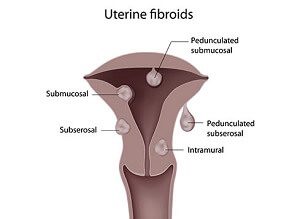 The diagnosis of uterine fibroids is established during the gynecological consultation based on the patient’s anamnesis and her clinical examination. The imaging investigations that confirm the diagnosis are represented by:
The diagnosis of uterine fibroids is established during the gynecological consultation based on the patient’s anamnesis and her clinical examination. The imaging investigations that confirm the diagnosis are represented by:
- Transvaginal ultrasound;
- Sonohysterography with physiological serum;
- Diagnostic hysteroscopy;
- Nuclear magnetic resonance or computer tomography of the pelvis.
The laboratory investigations represented by cytology in the liquid medium, biopsy of the uterine mucosa, and the determination of serum tumor markers have the role of excluding the existence of malignant tumors.
Hysterectomy is performed under general anesthesia, requiring a hospital stay of a variable duration of 3-5 days. Convalescence is of relatively short duration with the resumption of professional activity in a few weeks.
Recurrence of uterine fibroids, even after treatment, is not unusual, surgical intervention involving the surgical removal of the entire uterus being the only treatment that prevents the redevelopment of fibroids.
Signs that indicate the presence of a uterine fibroid
In many cases, fibroids do not cause symptoms. If they appear, the signs can be influenced by the location, size, and number of fibroids. The most common signs and symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
- menstrual periods that last more than a week;
- heavy menstrual bleeding;
- constipation;
- frequent urination;
- back pain or leg pain;
- feeling of pressure or pain in the pelvic area;
- problems during urination.
Can fibroids be prevented?
Until now, specialists have not been able to define a clear causality of the appearance of uterine fibroids and, implicitly, a proven system in the prophylaxis of this condition. Thus, it is considered that uterine fibroid cannot be prevented, the main solution remaining its detection through specific investigations and intervention with medicinal or surgical treatment, when necessary.
How can I save money?
In case you meet a certain sliding income scale, you may be able to get discounts and/or coupons from some drug manufacturers. In the situation when your doctor has you on prescription medication, it would be a good idea to ask him for the generic version or to talk with the drug company.
Not always will surgery be an option and your doctor may recommend medication to treat fibroma. So, take into consideration getting a second or even a third opinion.
If you are able to pay cash upfront you will be offered a discount by most clinics and hospitals.
Make sure you talk with your health insurance provider to see what and how much is covered by your policy. Some insurance companies may have strict rules on what you have to do for approving the surgery, while others may cover only certain procedures.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!